Qui il pdf con le caratteristiche del kit
trasferimento di energia senza fili. Fondata nel 2007, la società sta commercializzando
una tecnologia brevettata inventata da un team di fisici del MIT di fama mondiale. Questa
tecnologia utilizza il magnetismo per trasferire energia senza fili in un modo che è
sicuro, efficiente e che funziona a distanza.
una tecnologia brevettata inventata da un team di fisici del MIT di fama mondiale. Questa
tecnologia utilizza il magnetismo per trasferire energia senza fili in un modo che è
sicuro, efficiente e che funziona a distanza.
The System
The WiT-3300 Deployment Kit is a wireless “Park-and-Charge” self-charging system for electric vehicles. The system provides an efficient wireless energy transfer solution that completely avoids the need for the driver to plug in their battery electric vehicle or PHEV.
Benefits
- High efficiency (90% at 18cm)- High power transfer rates (up to 3.3kW)
- User friendly (tolerant to parking misalignment)
- Works through pavement (can be installed directly into a floor) and is weather resistant
- Safe for people and animals; minimal EMI
- Low implementation cost
- 4x smaller, 2x lighter, and more forgiving than traditional magnetic induction
Energy transfer over a distance and through paving materials
The WiT-3300 Deployment Kit is designed to transfer energy over distances ranging from 10-20cm, and custom configurations can be provided for vehicles having higher or lower ground clearance. Wireless energy transfer can occur through any non-metallic material, which means that the source device can be installed beneath a garage floor or paved parking space.
Technological Advantage
WiTricity’s patented energy transfer system does not require the source and capture resonator pairs to be perfectly aligned in order to achieve efficient energy transfer. In addition, our strongly coupled magnetic resonance energy transfer provides products which are 4x smaller, 2x lighter, and more efficient than solutions based on traditional magnetic induction.
Kit Includes
- (1) WiTricity wireless energy source, 15-20cm range
- (1) WiTricity energy capture
module, 15-20cm range
- (1) WiTricity RF Amplifier Assembly
- (1) WiTricity On-Vehicle Rectifier Assembly
- Full set of power cables for all components
- Users manual
WiTricity Safety
- Uses safe magnetic near field for energy transfer
- Highly Resonant coupling minimizes energy transfer to extraneous objects (not resonant)
- Designed to meet IEEE, FCC, and ICNIRP guidelines for human exposure
- Ideal for residential, municipal, and commercial
The Deployment Kit
The WiT-3300 Kit provides a complete set of wireless energy source and capture modules that can be integrated into an EV or PHEV for a truly wireless park-and-charge system.
The deployment kit can be purchased on its own or together with a complete WiT-3300 Evaluation System which includes the programmable DC Supply & Load, software to support testing, a resonator test bench, and accessories to support an in-depth evaluation.
Also available is the WiT-3300
Development System which in addition to the Evaluation System components, also includes our complete Design Documentation Package and in-depth technical training.
Putting Wireless Energy to Work
The WiT-3300 Deployment Kit enables users to evaluate, demonstrate, and develop applications for WiTricity’s patented (US 7,825,543 & US 7,741,734) and patent pending technology for wireless energy transfer. The kit demonstrates WiTricity’s unmatched ability to transfer energy over distance, through paving materials, and without requiring precise parking alignment.
Commercial use and sale of products based on WiTricity technology requires an IP license from WiTricity, or the purchase of licensed production level modules from WiTricity or other
authorized resellers and component manufacturers. Please contact WiTricity sales for further information regarding licensing and purchase of production volumes of components.
Attribute and Specifications
Operating Frequency: 145 kHz, nominal
Lateral Positional Tolerance: ±20 cm in vehicle side to side axis or ±10 cm in vehicle bumper to bumper axis
Output Power: DC, 300 watts-3.3 kilowatts, continuously variable
Output voltage: DC, 350 VDC- 400 VDC at 3.3 kW, 18 cm resonator-resonator distance
Physical Dimensions:
Source Module Enclosure 50 cm x 50 cm x 3.75 cm; 12.5 kg
Capture Module Enclosure 50 cm x 50 cm x 3.75 cm; 12.5 kg
RF Amplifier Assembly 22 cm x 33 cm x 13 cm; 4.2 kg
On-Vehicle Rectifier Assembly 20 cm x 28 cm x 7 cm; 3.6 kg
Ricarica wireless su iPhone: e se fosse WiTricity?

Sapevamo già che iPhone 5 (o per meglio dire, la generazione che arriverà nel 2012) dovrebbe implementare un "nuovo modo di ricaricare il telefono", e qualcuno azzarda che possa trattarsi di una tecnologia davvero innovativa e molto diversa rispetto a quanto visto nei prodotti della concorrenza. Riflettori puntati verso WiTricity.
A differenza del Palm Pre o del TouchPad, i cui caricabatteria ad induzione elettromagnetica richiedono comunque il contatto fisico col dispositivo, la cosiddetta Wireless Electricity consente invece di irraggiare il flusso elettrico in modo sicuro -almeno così affermano i suoi creatori- e per distanze notevoli. Nata da alcune importanti ricerche effettuate al MIT e commercializzata col brand WiTricity, questa tecnologia consente di ricaricare le batterie fino a due metri di distanza:
I campi magnetici di due dispositivi disegnati all'uopo con frequenze di risonanza strettamente correlate possono unirsi in un unico, continuo campo magnetico. Il team del Prof. Soljačić ha dimostrato come utilizzare questo fenomeno per consentire il trasferimento dell'energia da un dispositivo all'altro con alta efficienza e su distanze che risultano più utili nel mondo delle applicazioni reali.
Alla startup sono interessati in parecchi, soprattutto in seguito alla sua presentazione al TED 2009, compresi colossi del calibro di Intel eToyota, e la stessa Apple possiede nel proprio arsenale di brevetti un documento intitolato "Wireless power utilization in a local computing environment" che porta espliciti riferimenti alle ricerche effettuate al MIT.
Come al solito, è difficile stabilire se queste innovazioni approderanno mai sugli scaffali dell'Apple Store, ma le aspettative in ballo sono alte, e non solo a Cupertino. In futuro potremmo utilizzare tastiere e mouse senza batterie, oppure ricaricare al contempo iPhone ed iPad semplicemente ponendoli davanti allo schermo dell'iMac. Al netto delle implicazioni sulla salute, tutte ancora da valutare, se non è fantascienza questa, poco ci manca.
SAE taskforce developing standards for wireless charging for plug-in vehicles; targeting first guideline by end of 2011
In January SAE has launched a taskforce (SAE J2954) on the “Wireless Charging of Electric and Plug-in Electric Vehicles”—i.e. EVs and PHEVs. The taskforce, which launched in October 2010 and began meeting in November 2010, has a goal of delivering the first SAE guideline by end of 2011 for publishing in 2012. Since additional field data is needed for standardization, said Jesse Schneider of BMW, leader of the J2954 effort, a 2012-13 date is estimated for the balloted standard.
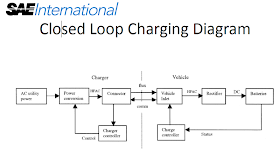 |
| Closed loop wireless charging diagram. Source: Jesse Schneider |
The taskforce goal is to establish performance and safety limits for wireless power transfer for automotive applications while establishing a minimum interoperability requirement. The team is currently reviewing the state of the art of wireless charging (e.g., inductive, magnetic resonance) and compiling an interoperability study.
The scope of the work covers light duty passenger EVs and PHEVs and buses. Charging locations to be considered include residential; on-road (static and dynamic), with Level 1, 2 and 3 capability (the last for buses). Presently the J2954 team is a cross-industry team of auto and bus OEMs, EV infrastructure companies, government laboratories, universities, wireless power and Tier 1 suppliers.
Many of the OEMs and EV infrastructure companies have already signed on to this. This taskforce is also taking an active role to work from the onset with ISO standards and VDE (German standards) to harmonize this important new trend.—Jesse Schneider, Chair SAE J2954
| Two wireless options |
|---|
| Inductive charging uses the electromagnetic field to transfer energy between two objects in close proximity. |
| A charging station sends energy through inductive coupling to an electrical device, which stores the energy in the batteries. |
| Magnetic resonance uses the magnetic coupling of two objects exchanging energy through their varying or oscillating magnetic fields. Resonant coupling occurs when the natural frequencies of the two objects are approx. the same. |
Currently, SAE 1773 defines a standard for EV inductive coupled charging. The standard was based upon specific hardware (paddle charger); vehicle-station bidirectional communication was either RF or IrDA. SAE 1772 specifies a conductive charge coupler standard that is not compatible to ISO standard in Europe.
Standard charging could be in the up to ~4 kW range, Schneider says, with Level 3 fast charging of up to 60 kW possible for buses, for example. Passenger vehicles could be wirelessly charged during work, parking garage, home use, similar to conductive charging (such as SAE 1772) at a higher power level, with vehicle approval.
This wireless charging effort is different than the conductive plug charging standardization underway in that harmonization is seen as first priority, Schneider said. The SAE J2954 taskforce has established a relationship with ISO/IEC and VDE (German Standard) to ensure open communication to expedite harmonization. VDE is planning to publish their whitepaper on wireless charging for Germany in the first quarter of 2011 and ISO & IEC are planning to standardize in the coming years.
Resources
- SAE TIR J2954: “Wireless Charging of Electric and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles” (presentation by Jesse Schneider)
Nessun commento:
Posta un commento